PROCEDURES
I perform a wide range of gynaecological procedures including complex gynaecological surgery. I am accredited to perform the highest level of advanced laparoscopic surgery (AGES/RANZCOG Level 6) and I hold certification as a robotic surgeon with the Da Vinci robotic system. I have expertise in all areas of minimally invasive surgery, with special interests in laparoscopic and robotic hysterectomy, myomectomy and treatment of endometriosis.
Further information on procedures can be found at the following:
https://ranzcog.edu.au/womens-health/patient-information-guides/patient-information-pamphlets
https://www.aagl.org/patient-information-sheets/
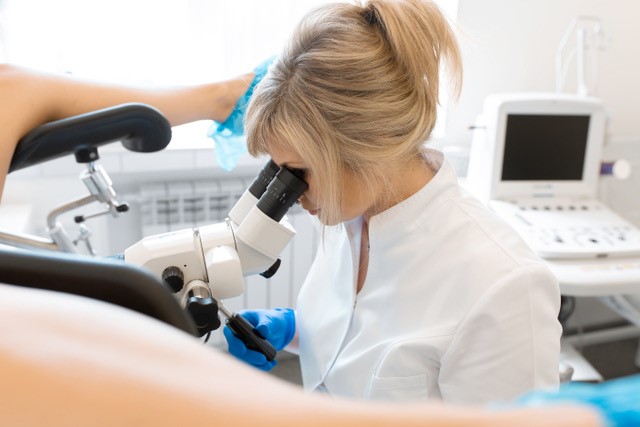 |
COLPOSCOPY Women with abnormal cervical screening tests are recommended to have a colposcopy. Colposcopy is performed at the specialist rooms using a machine called a colposcope, which is essentially a microscope that magnifies the cervix so that abnormal changes can be detected. The procedure is similar to having a cervical smear test and usually takes 10-15 minutes. Specific fluids may be applied to the cervix and vagina to help detect abnormal areas. Sometimes, biopsies of the cervix are required to further analyse any abnormal areas. These may cause minor discomfort or cramping which usually subside with simple analgesia such as paracetamol or ibuprofen. It is important not to insert anything into the vagina (this includes sexual intercourse and tampons) for a week after a biopsy in order to prevent bleeding and infection. |
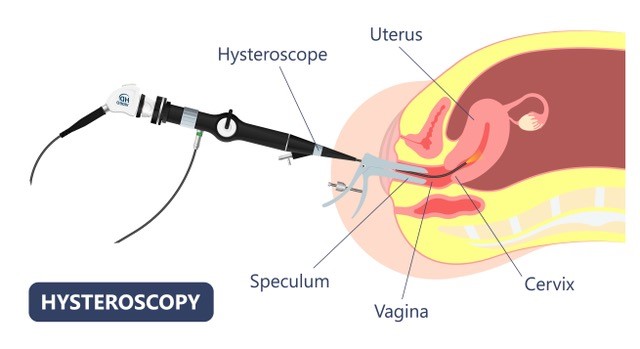 |
HYSTEROSCOPY Hysteroscopy is a day procedure where a thin camera (hysteroscope) is inserted vaginally and passed through the cervix to visualise the internal cavity of the uterus. It may be performed for diagnostic reasons but can also be used for treatment procedures including:- Polypectomy (removal of polyps) – Myomectomy (removal of fibroids which are inside the uterine cavity) – Endometrial ablation (removal of the lining of the uterus using radiofrequency or diathermy) – Septoplasty (removal of uterine septum) – Adhesiolysis (removal of intrauterine adhesions, treatment of Ashermann’s syndrome) – Retrieval of IUDs Learn more: https://ranzcog.edu.au/RANZCOG_SITE/media/RANZCOG-MEDIA/Women%27s%20Health/Patient%20information/Hysteroscopy-pamphlet.pdf?ext=.pdf |
 |
LAPAROSCOPY
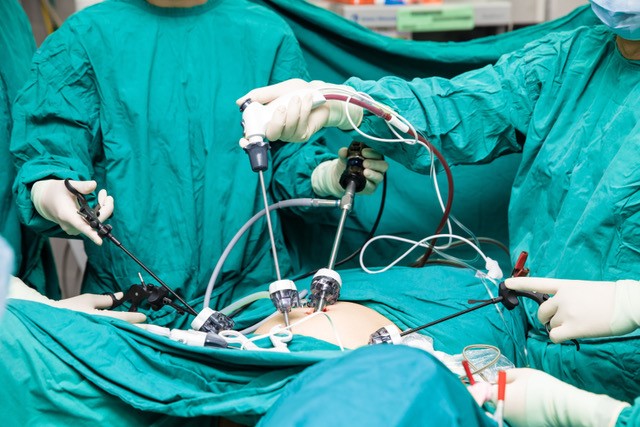
Often called “keyhole surgery”, laparoscopy is a procedure where a surgical telescope (camera) and other instruments are inserted through small incisions (usually a centimetre or less) in the abdominal wall. The abdomen is inflated with carbon dioxide gas to allow the surgeon to see and operate on the pelvic organs. Compared with traditional open abdominal surgery, laparoscopy has the following advantages for patients: Laparoscopy can be used to perform many gynaecological procedures including endometriosis surgery, hysterectomy, prolapse surgery, removal of ovarian cysts, removal of fibroids, division of adhesions (internal scar tissue), tubal ligation, and assessment of pelvic pain and infertility. |
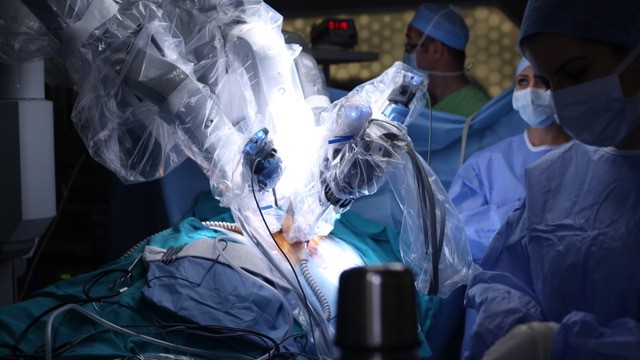 |
ROBOTIC ASSISTED LAPAROSCOPY Surgical robots have been developed to enhance the performance of laparoscopy and allow surgeons to perform procedures with more precision, flexibility and control than conventional laparoscopy. This technique uses the same small incisions in the abdominal wall to allow a telescopic camera and instruments to be used to perform pelvic surgery. The advantages of the robotic system over laparoscopy include: • 3D high resolution vision • Wristed instruments which allow seven degrees of motion • Improved ergonomics Studies have shown that robotic surgery is associated with less blood loss and even shorter length of hospital stay than laparoscopic surgery in some gynaecological procedures. This cutting edge technology also allows surgeons to perform extremely complex surgery which might have otherwise required an open cut into the abdomen.Robotic assisted laparoscopy can be used to perform many different procedures, including hysterectomy, endometriosis surgery, removal of fibroids, and prolapse surgery. Learn more: |
 |
MYOMECTOMY This is a surgical procedure to remove fibroids from the uterus. It may be performed via an open abdominal incision (laparotomy), via keyhole surgery (laparoscopy), or via robotic surgery. The route of surgery which is most appropriate depends on the individual patient and the size, number and location of the fibroids. Learn more: https://www.aagl.org/patient/Laparoscopic-or-Robotic-Myomectomy-AAGL.pdf |
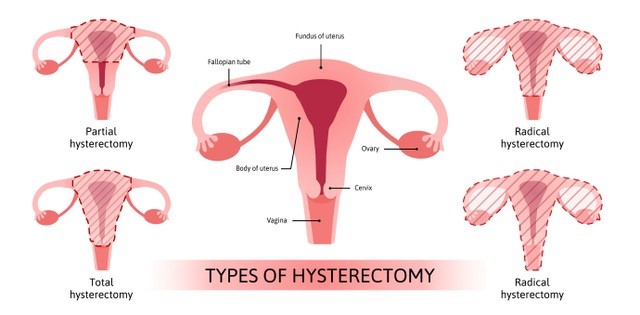 |
HYSTERECTOMY This is a surgical procedure to remove the uterus. There are various forms of hysterectomy: • Total hysterectomy – removal of uterus and cervix • Subtotal hysterectomy – removal of uterus but not the cervix A hysterectomy can be performed with removal of the fallopian tubes (bilateral salpingectomy) and removal of the ovaries (bilateral oophorectomy) if required. There are several different routes of performing a hysterectomy: • Vaginal • Abdominal • Laparoscopic • Robotic-assisted laparoscopic The route of surgery depends of various different factors including the size and position of the uterus, presence of fibroids, the presence of prolapse, previous surgery and other factors. Learn more: https://ranzcog.edu.au/RANZCOG_SITE/media/RANZCOG-MEDIA/Women%27s%20Health/Patient%20information/Hysterectomy-pamphlet.pdf?ext=.pdf |
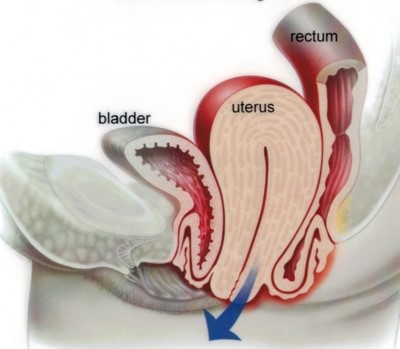 |
PROLAPSE SURGERY Surgery for prolapse conditions can vary depending on the type of prolapse and on individual patient characteristics. Procedures for prolapse include: • Vaginal repair (anterior or posterior) • Sacrospinous fixation • Uterosacral ligament suspension • Sacrocolpopexy A hysterectomy may be performed at the same time. Learn more: https://ranzcog.edu.au/RANZCOG_SITE/media/RANZCOG-MEDIA/Women%27s%20Health/Patient%20information/Pelvic-Organ-Prolapse-KK19.pdf?ext=.pdf |

